Umbilical Cord Lining
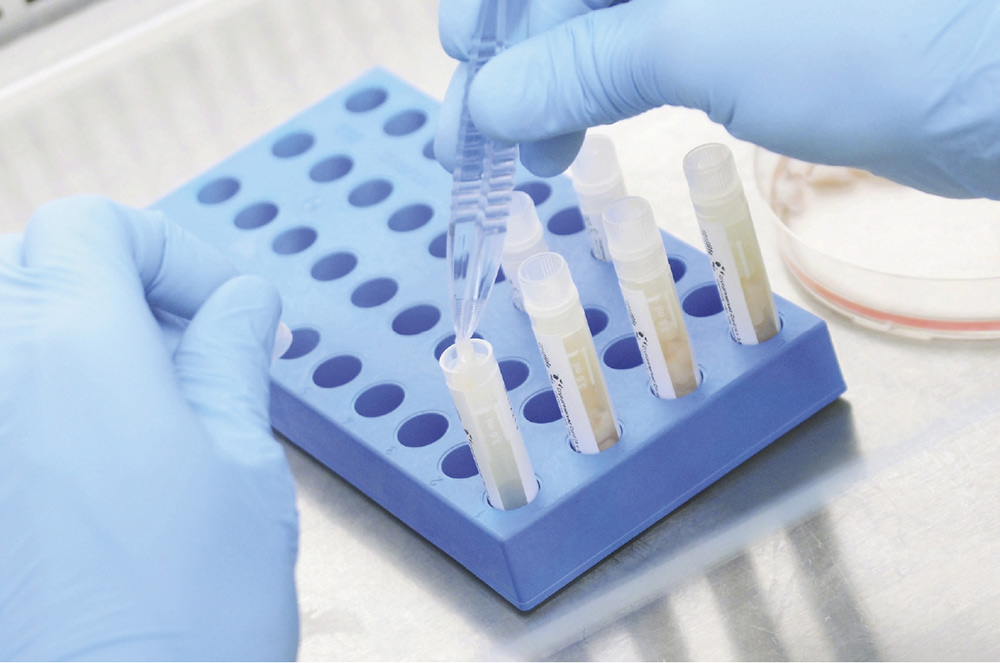
Along with banking the umbilical cord blood itself, families now have the option to also bank a section of the actual tissue that makes up the umbilical cord. Umbilical cord lining is the membrane that covers the umbilical cord. As with cord blood, the collection process for cord lining is fast, easy, and painless.
Give your baby a lifetime of protection by banking with Cordlife today.
What is Umbilical Cord?
The umbilical cord is the connecting cord from the developing fetus to the placenta which allows blood to carry oxygen and nutrition to the baby in the womb. After the baby is delivered, the umbilical cord is cut and normally discarded with the placenta as medical waste until researchers became aware of its medical potential.
Along with banking the umbilical cord blood itself, families now have the option to also bank a section of the actual tissue that makes up the umbilical cord. Umbilical cord lining is the membrane that covers the umbilical cord. As with cord blood, the collection process for cord lining is fast, easy, and painless
What are Umbilical Cord Lining Stem Cells?
Cord Lining contains a high numbers of Epithelial Stem cells (EpSCs) and Mesenchymal (MSCs) stem cells which have shown immense potential in aiding the repair of injured tissues and organs and the treatment of various diseases. EpSCs form the soft tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body including cornea, skin, and liver. MSCs are the building blocks of structural tissues of our body such as bone, cartilage, muscle, fibrous tissues and fat. Scientist believe that the cord lining also contains other types of cells which may be useful but have yet to be discovered.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
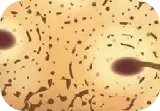




Cord lining epithelial stem cells (CLEpSCs)

Why do parents save their baby's cord blood and cord lining?
Rich source of stem cells
Your baby’s umbilical cord has the youngest and most active stem cells compared with other stem cell sources such as embryo, bone marrow, and peripheral blood.

Proven use in transplants
More than 80 diseases can potentially be treated with cord blood, and 60,000 transplants have taken place worldwide.

Untapped clinical potential
Researchers all over the world are learning how to use stem cells to treat more diseases and repair damaged tissue or organs.

Treatment options for the family
The stem cells you stored are a perfect match for your baby, and they could be used to treat other members of your family.

Readily available for a lifetime
Stem cells can be kept indefinitely if they are properly stored, and you can retrieve them whenever you need them.
WHY CORDLIFE?

23 Years of Experience
Cordlife is the first cord blood bank in Singapore, and a leading industry player in Asia.

Proven Global Expertise
Cordlife has released more than 77 cord blood units to 21 healthcare institutions in 10 countries.

Accredited Facility
Cordlife Hong Kong has AABB accreditation, giving you peace of mind.

Listed on Singapore Exchange
We’ve strengthened our financial position to ensure that we’ll be here with you for a long time.

Seven Facilities in Asia
We own a network of stem cell cryopreservation facilities across Asia, and our facilities serve as back-up for one another in the event of an emergency.
Technology Pioneer
We were recognised by the World Economic Forum for our contributions to the field of cellular therapy
Trusted by more than 600,000 parents in Asia.






